Published 31 August 2023
Defeating the Enemy Within: Treating Infected Bed Sores Made Easy
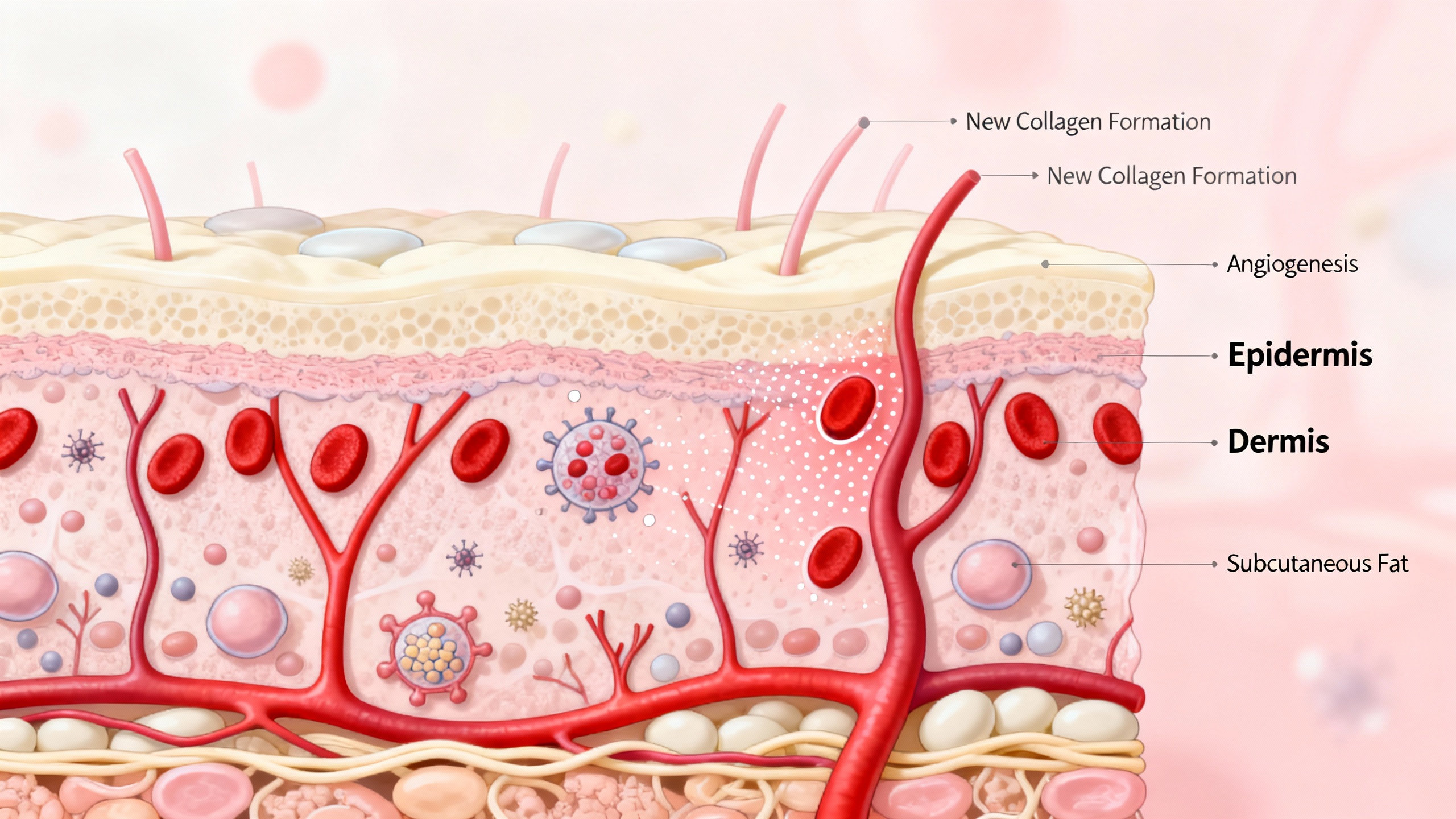
Understanding Bed Sores
Bed sores, also known as pressure ulcers or decubitus ulcers, are a common concern for individuals who are bedridden or have limited mobility. These sores develop when there is prolonged pressure on certain areas of the body, leading to tissue damage. Understanding the causes and stages of bed sores is essential for effective treatment and prevention.
What Are Bed Sores?
Bed sores are localized areas of damaged skin and underlying tissue caused by pressure, friction, or shear forces. They typically occur on bony prominences such as the hips, tailbone, heels, and elbows. The constant pressure on these areas restricts blood flow, leading to tissue death and the formation of open wounds.
Bed sores can range in severity from mild inflammation to deep, open wounds that expose muscles and bones. Left untreated, they can be painful, prone to infection, and slow to heal. It’s crucial to address bed sores promptly to prevent complications and promote healing.
Causes of Bed Sores
The primary cause of bed sores is pressure on the skin and underlying tissues. This pressure disrupts blood flow, depriving the cells of oxygen and nutrients necessary for healthy tissue maintenance. Other contributing factors include friction, shear forces, moisture, poor nutrition, and compromised immune function.
Individuals who are bedridden, have limited mobility, or spend prolonged periods in a wheelchair are at a higher risk of developing bed sores. Factors such as advanced age, chronic medical conditions, and malnutrition can further increase the risk.
Stages of Bed Sores
Bed sores progress through different stages, each characterized by the severity of tissue damage. The stages are commonly classified as follows:
-
Stage 1: At this stage, the skin appears red or discolored and may feel warmer or firmer to the touch. The affected area may also be itchy or painful, indicating early tissue damage.
-
Stage 2: The skin now shows signs of blistering or open sores, often accompanied by shallow craters or shallow ulcers. The surrounding skin may be red and swollen.
-
Stage 3: The ulcer deepens, extending into the underlying tissue layers. The wound may appear as a crater with visible fat, but bones, tendons, or muscles are not exposed.
-
Stage 4: This is the most severe stage, where the ulcer extends deep into the tissue, exposing bones, tendons, or muscles. The wound may be accompanied by a foul odor and significant drainage.
Understanding the stages of bed sores is important for proper assessment and treatment. It’s crucial to seek medical attention if you notice any signs of infection or if the bed sores progress to more advanced stages. For more information on preventing bed sores, refer to our article on preventing pressure sores.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of bed sores, their causes, and the stages of progression, individuals can take the necessary steps to manage and prevent these challenging skin conditions.
Recognizing and Treating Infected Bed Sores
When it comes to managing and treating infected bed sores, early detection is key. In this section, we will discuss the signs of infection, when to seek medical help, and effective methods for treating infected bed sores.
Signs of Infection
It’s important to closely monitor bed sores for any signs of infection. Some common signs include:
- Increased pain and tenderness around the affected area.
- Swelling, redness, or warmth around the wound.
- Pus or discharge with a foul odor.
- Fever or an overall feeling of illness.
- Delayed healing or the formation of new sores in the surrounding area.
- Red streaks extending from the wound.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s crucial to take immediate action to prevent the infection from worsening.
When to Seek Medical Help
While minor bed sores can often be managed at home, it’s important to know when to seek medical help. You should consult a healthcare professional if:
- The bed sore worsens or does not show signs of improvement.
- The area around the wound becomes increasingly red, swollen, or warm.
- The pain or discomfort becomes severe.
- You notice any signs of infection, such as pus, odor, or red streaks.
- You develop a fever or experience other symptoms of illness.
Prompt medical attention can help prevent complications and ensure appropriate treatment for the infected bed sore.
Treating Infected Bed Sores
Treating an infected bed sore requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the wound and the underlying infection. The specific treatment plan may vary based on the severity of the infection and the individual’s overall health. A healthcare professional will typically:
-
Clean the wound: The infected area will be gently cleaned with a mild saline solution or an antiseptic solution to remove debris and bacteria. This helps prevent further infection and promotes healing. For more information on wound cleaning and dressing, refer to our article on bed sore dressings and bandages.
-
Apply topical medications: Depending on the severity of the infection, your healthcare provider may prescribe or recommend topical medications such as antibacterial creams or ointments. These medications aid in controlling the infection and promoting healing.
-
Administer oral or intravenous antibiotics: In cases where the infection is severe or has spread beyond the wound, oral or intravenous antibiotics may be necessary to combat the infection. These medications are prescribed by a healthcare professional and should be taken as directed.
-
Manage pain and discomfort: Pain management plays a crucial role in the treatment of infected bed sores. Your healthcare provider may recommend pain relievers or suggest other strategies for managing pain. For more information on relieving pain caused by bed sores, refer to our article on relieving pain from pressure ulcers.
-
Promote wound healing: To aid in the healing process, your healthcare provider may suggest additional measures such as regular wound dressing changes, the use of specialized dressings, or the application of ointments that promote tissue regeneration. Adequate nutrition and hydration are also essential for optimal wound healing. For more information on promoting healing, refer to our article on nutrition and hydration.
Remember, it’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and attend follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing of the infected bed sore. Effective treatment requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the wound and any underlying infection. By seeking timely medical help and following the recommended treatment plan, you can effectively manage and treat infected bed sores.
Managing Symptoms and Promoting Healing
When it comes to treating infected bed sores, there are several essential steps to manage symptoms and promote healing. These include cleaning and dressing wounds, relieving pressure and promoting blood circulation, and ensuring proper nutrition and hydration.
Cleaning and Dressing Wounds
Cleaning and dressing wounds is a crucial part of managing infected bed sores. This process involves gently cleansing the wound with a mild antiseptic solution or sterile saline to remove any debris or bacteria. It’s important to avoid using harsh cleansers or scrubbing the wound, as this can further irritate the skin.
After cleaning, it’s essential to apply an appropriate dressing to the wound. The type of dressing used will depend on the stage of the bed sore and the amount of exudate (drainage) present. Dressings can help create a moist healing environment, protect the wound from external contaminants, and promote the growth of new tissue. Consult with a healthcare professional or wound care specialist to determine the most suitable dressing for your specific situation.
Relieving Pressure and Promoting Blood Circulation
Relieving pressure on the affected area is crucial for the healing of bed sores. This can be achieved by using specialized support surfaces, such as pressure-relieving mattresses or cushions, that distribute pressure evenly and reduce the risk of further damage to the skin. Regular repositioning and movement are also essential to prevent prolonged pressure on any one area.
In addition to relieving pressure, promoting blood circulation is vital for healing bed sores. Gentle massage and range-of-motion exercises can help improve blood flow to the affected area, aiding in the delivery of oxygen and nutrients necessary for tissue repair. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist for guidance on appropriate exercises and techniques.
Nutrition and Hydration
Proper nutrition and hydration play a significant role in the healing of bed sores. A well-balanced diet that includes an adequate intake of protein, vitamins, and minerals is essential for supporting the body’s healing process. Protein, in particular, is crucial for tissue repair and regeneration. Consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional to ensure you are receiving the necessary nutrients for optimal wound healing.
Staying hydrated is equally important, as it helps maintain the elasticity of the skin and promotes overall health. Aim to drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day and include hydrating foods, such as fruits and vegetables, in your diet.
By effectively managing symptoms and promoting healing through proper wound care, pressure relief, and a nutritious diet, you can support the healing process of infected bed sores. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options to ensure the best possible care.
Preventing Bed Sores
When it comes to preventing bed sores, taking proactive measures is essential. By implementing preventive strategies, you can reduce the risk of developing these painful and potentially dangerous wounds. Here are three key approaches to preventing bed sores: regular positioning and movement, proper skin care and hygiene, and support surfaces and equipment.
Regular Positioning and Movement
One of the most effective ways to prevent bed sores is by ensuring regular positioning and movement. Prolonged pressure on specific areas of the body can lead to the development of bed sores. By changing positions frequently, weight is redistributed, reducing the pressure on any one area.
For individuals who are bedridden or have limited mobility, it’s crucial to reposition them at least every two hours. This can be achieved by using assistive devices such as bed rails, turning sheets, or specialized cushions. Regular turning and repositioning not only alleviate pressure on vulnerable areas but also promote blood circulation, which aids in preventing bed sores.
Proper Skin Care and Hygiene
Maintaining proper skin care and hygiene is paramount in preventing bed sores. Clean and healthy skin is less prone to breakdown and infection. To keep the skin in optimal condition, follow these guidelines:
-
Keep the skin clean: Gently cleanse the skin with a mild, pH-balanced cleanser and warm water. Avoid using harsh soaps or excessive scrubbing, as they can strip the skin’s natural protective oils.
-
Moisturize regularly: Apply a moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated and supple. Look for products specifically formulated for sensitive or dry skin. Avoid applying moisturizer to areas at high risk for bed sores, as excess moisture can contribute to skin breakdown.
-
Inspect the skin daily: Regularly examine the skin for any signs of redness, irritation, or early stage bed sores. If any abnormalities are detected, promptly address them to prevent further progression.
-
Avoid excessive moisture and friction: Keep the skin dry and minimize friction by using moisture-wicking bedding materials and proper positioning techniques. This reduces the risk of skin breakdown and irritation.
Support Surfaces and Equipment
The selection of appropriate support surfaces and equipment is crucial in preventing bed sores. These aids help distribute pressure evenly and provide added support to vulnerable areas. Consider the following options:
-
Pressure-relieving mattresses: Choose mattresses designed to distribute pressure evenly, such as air mattresses, foam mattresses, or alternating pressure mattresses. These specialized surfaces help reduce the risk of bed sores by minimizing pressure on specific areas of the body.
-
Cushions and overlays: Utilize cushions and overlays specifically designed for pressure redistribution. These products are available in various shapes and materials to provide additional support and reduce pressure on high-risk areas.
-
Wheelchair cushions: For individuals using wheelchairs, investing in appropriate wheelchair cushions is essential. These cushions help distribute pressure and minimize the risk of bed sores, especially in areas prone to pressure, such as the buttocks and tailbone.
By implementing regular positioning and movement, maintaining proper skin care and hygiene, and utilizing suitable support surfaces and equipment, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing bed sores. Remember, prevention is key in managing this condition. For more information on preventing bed sores, check out our article on preventing pressure sores.
Coping with Bed Sores
Living with bed sores can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. It’s important to address not only the physical symptoms but also the emotional well-being of individuals dealing with bed sores. Here are some key aspects to consider when coping with bed sores: emotional support and mental health, pain management, and rehabilitation and physical therapy.
Emotional Support and Mental Health
Dealing with bed sores can take a toll on a person’s emotional well-being. Feelings of frustration, sadness, and isolation are common. It is important to seek emotional support from loved ones, friends, or support groups. Talking about your feelings and concerns with someone who understands can provide comfort and help you cope with the challenges you’re facing. If needed, consider seeking professional help from a counselor or therapist who specializes in emotional support for individuals with chronic conditions.
Pain Management
Bed sores can be painful, and managing pain is an essential part of coping with this condition. Pain management techniques can range from over-the-counter pain relievers to prescription medications, depending on the severity of the pain. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper assessment and guidance on pain management strategies. They may recommend topical creams, dressings, or other interventions to relieve pain caused by bed sores. Our article on relieving pain from pressure ulcers provides further insights into pain management techniques.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Rehabilitation and physical therapy play a crucial role in the healing and recovery process for individuals with bed sores. These therapies focus on improving mobility, strength, and overall physical well-being. A physical therapist or rehabilitation specialist can design a personalized exercise program to help prevent further complications and promote healing. They may also provide guidance on proper body positioning and movement techniques to relieve pressure on the affected areas. For more information on exercises and techniques to prevent bed sores, refer to our article on bed sore prevention exercises.
Incorporating rehabilitation and physical therapy into the care plan can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with bed sores. These therapies not only aid in the healing process but also help prevent future occurrences and promote overall well-being.
Remember, coping with bed sores requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects. By seeking emotional support, managing pain effectively, and engaging in rehabilitation and physical therapy, individuals can enhance their ability to cope with the challenges of bed sores and work towards a better quality of life.
